Bird Vocab
A
Asymmetrical. Not the same on both sides, as in the ear placement of some owls.
B
Beak. The shorter, hooked bill of a raptor or parrot.
Bill. The jaws of a bird, including their horny covering.
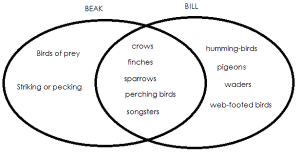
Difference between Beak and Bill: “In Ornithology, beak is the general term applicable to all birds; in ordinary language beak is always used of birds of prey, and generally when striking or pecking is in question; beak and bill are both used of crows, finches, sparrows, perching birds and songsters generally, bill being however more frequent; bill is almost exclusively used of humming-birds, pigeons, waders, and web-footed birds.”
Birder. The acceptable term used to describe the person who seriously pursues the hobby of birding. May be professional or amateur.
Birding. A hobby in which individuals enjoy the challenge of bird study, listing, or other general activities involving bird life.
Bird-watcher. A rather ambiguous term used to describe the person who watches birds for any reason at all, and should not be used to refer to the serious birder.
Brood. The young birds hatched from a group of eggs in a single nest, usually laid by one female.
C
Chasing. American term used to mean “the pursuit of a previously located rare bird.”
Crest. The showy growth of feathers on the head of the bird.
Crop. A saclike area beneath the throat used to store undigested food.
Crown. The top of the head of a bird.
D
Dip. To miss out on seeing an expected bird; or the bird that was missed.
Down. Soft, fluffy feathers on a young bird or the layers of insulating feathers beneath an adult’s outer feathers.
F
Fledgling. A young bird that has grown its first complete set of flight feathers and has left the nest.
FOY. Stands for “first of year” as in the first encounter with a particular bird in a calendar year; seeing certain birds can indicate seasonal changes.
G
Gizzard. The large part of the bird’s digestive system, where food is ground into small pieces.
Gland. A part of the body that produces a substance for a particular purpose, such as oil for waterproofing a bird’s feathers.
Granary tree. A tree Acorn Woodpecker’s use to drill hundreds and thousands of holes in to store just as many acorns for the winter.
H
Hatch. To emerge from an egg.
Hover. To hang in the air on fluttering wings.
I
Incubate. To sit on eggs to hatch them by warmth.
L
Lore. The region between the eyes and nostrils of bird.
M
Migrate. To move from one region to another, often on a regular schedule for feeding or breeding.
N
Nestling. A young bird that has not left the nest.
P
Parliament. A group of owls.
Patagial marks. Leading edge of a birds wing between the “shoulder” and the “wrist.” Red-tailed Hawk’s patagial marks are visible during flight.
Pellet. Material that cannot be digested and was thrown up by a bird of prey.
Plumage. The term for all of the feathers that cover a bird’s body.
R
Raptor. A bird of prey that kills and eats other animals; it usually has keen eyesight, a hooked beak, and sharp talons.
Rookery. A communal nesting ground for gregarious birds consisting of anywhere from just a few nests to hundreds of nesting pairs. Used by a number of bird species, most notably herons, egrets and cormorants, as well as several types of corvids.
S
Suet. Hard animal fat.
T
Talon. The claw of a bird of prey.
Twitching. British term used to mean “the pursuit of a previously located rare bird.”
W
Whitewash. Owl excrement; often found along with pellets under an owl’s favorite perch, sometimes mistaken for tree sap.
Here is a link to a MEGA birding glossary. And for even more fun, here is a link to twitchers’ vocabulary.
Enjoy
*Terms not linked to sources retrieved from: Kurki, Kim. World of Birds: A Beginner’s Guide. Black Dog & Leventhal Publishers, Inc, 2014. Print.